A Genomic Language Model for Chimera Artifact Detection in Nanopore Direct RNA Sequencing
Oct 26, 2024·, ,,,,·
1 min read
,,,,·
1 min read
Yangyang Li
Ting-You Wang
Qingxiang (Allen) Guo
Yanan Ren
Xiaotong Lu
Qi Cao
Rendong Yang
Abstract
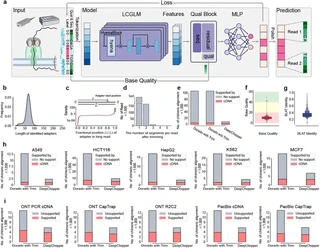
Chimera artifacts in nanopore direct RNA sequencing (dRNA-seq) can significantly distort transcriptome analyses, yet their detection and removal remain challenging due to limitations in existing basecalling models. We present DeepChopper, a genomic language model that precisely identifies and removes adapter sequences from base-called dRNA-seq long reads at single-base resolution, operating independently of raw signal or alignment information to effectively eliminate chimeric read artifacts. By removing these artifacts, DeepChopper substantially improves the accuracy of critical downstream analyses, such as transcript annotation and gene fusion detection, thereby enhancing the reliability and utility of nanopore dRNA-seq for transcriptomics research.
Type
Publication
bioRxiv
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.23.619929
Preprint page: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.10.23.619929v1
PDF: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.10.23.619929v1.full.pdf
Authors
Authors

Authors
Qingxiang (Allen) Guo
(he/him)
Postdoctoral Scholar | Cancer Genomics & AI
Postdoctoral scholar at Northwestern University developing computational approaches for cancer genomics.
My research integrates long-read sequencing, structural variant analysis, and deep learning to decode
the regulatory complexity of cancer genomes.
Authors
Authors
Authors
Authors